What’s Powering the Rapid Expansion of the Global Amines Market Across Multiple Industries?
Author : komal Galande | Published On : 19 Feb 2026
Future of Executive Summary Amines Market: Size and Share Dynamics
Data Bridge Market Research analyses that the amines market is expected to reach USD 26,794.05 million by 2030, which was USD 19,578.15 million in 2022, registering a CAGR of 4.00% during the forecast period of 2023 to 2030
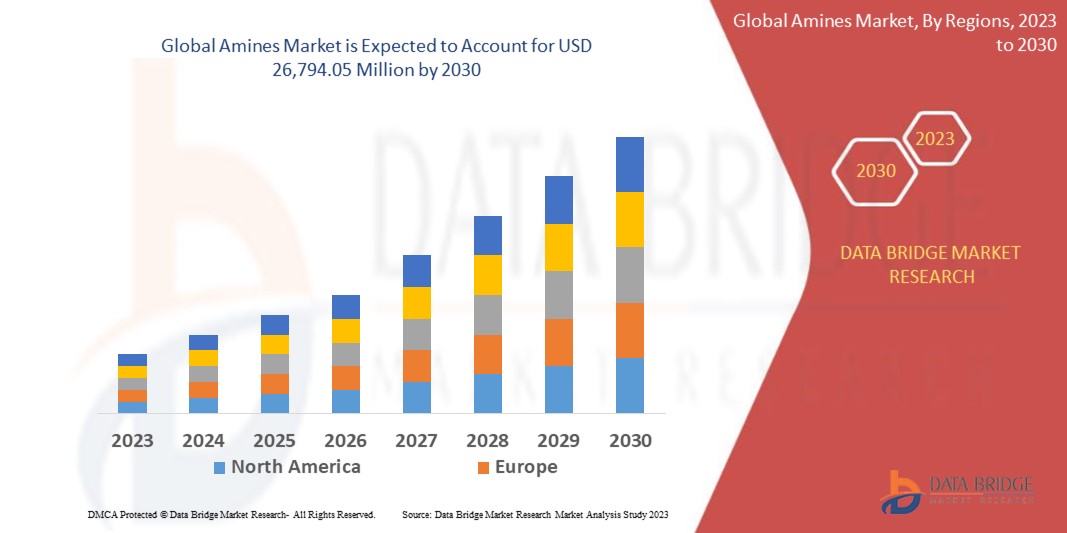
The Amines business document lists and studies the leading competitors and also provides the insights with strategic industry analysis of the key factors influencing the market dynamics. This market research report provides granular analysis of the market share, segmentation, revenue forecasts, and geographic regions of the market. The report comprises a professional and in-depth study on the current state, which focuses on the major drivers and restraints for the key players. The influential Amines Market analysis report takes into account several key manufacturers, which are based on company profile, sales data, product specifications,, etc.
A winning Amines Market report all-inclusively estimates general market conditions, the growth prospects in the market, possible restrictions, significant industry trends, market size, market share, sales volume, and future trends. Analysis of major challenges currently faced by the business and the possible future challenges that the business may have to face while operating in this market are also taken into account. This Amines Market research report encompasses a comprehensive study of the product specifications, revenue, cost, price, gross capacity, and production. Acquiring valuable market insights with the new skills, latest tools, and innovative programs is sure to help achieve business goals.
Tap into future trends and opportunities shaping the Amines Market. Download the complete report:
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-amines-market
Amines Market Environment
Segments
- By Type: The amines market can be segmented into primary amines, secondary amines, tertiary amines, and specialty amines. Primary amines are expected to dominate the market due to their widespread applications in various industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and personal care.
- By Application: Based on application, the market can be segmented into agricultural chemicals, water treatment, personal care, cleaning products, and others. The agricultural chemicals segment is anticipated to witness significant growth owing to the increasing demand for agrochemicals to improve crop yield.
- By End-Use Industry: The amines market can also be segmented by end-use industry into agriculture, pharmaceuticals, chemical, and others. The agriculture industry is expected to be the largest consumer of amines, primarily driven by the need for fertilizers and pesticides.
Market Players
- BASF SE: A leading player in the amines market, BASF SE offers a wide range of amines for diverse applications. The company focuses on product innovation and expansion to cater to the evolving market demand.
- The Dow Chemical Company: With a strong presence in the global amines market, The Dow Chemical Company is known for its high-quality amines used in various industries. The company emphasizes sustainability and technological advancements in its product offerings.
- Akzo Nobel N.V.: Akzo Nobel N.V. is a key player in the amines market, offering a comprehensive portfolio of amines for different applications. The company has a global presence and invests in research and development to enhance its product offerings.
- Huntsman Corporation: Huntsman Corporation is a prominent player in the amines market, known for its innovative solutions and quality products. The company focuses on collaborations and partnerships to strengthen its market position.
The global amines market is witnessing growth due to the increasing demand for amines in various industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. Factors such as population growth, urbanization, and industrialization are driving the demand for amines for applications like agrochemicals, water treatment, and personal care products. Key market players are focusing on strategic initiatives such as product launches, acquisitions, and partnerships to gain a competitive edge in the market. Overall, the global amines market is poised for significant growth in the coming years.
DDDDDThe global amines market is currently experiencing a notable upsurge due to the escalating demand for amines across multiple industries, particularly in agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. This surge can be attributed to several key factors such as the rapid population growth, expanding urbanization, and increasing industrial activities. These factors have collectively fueled the need for amines in diverse applications like agrochemicals, water treatment, and personal care products. As a result, market players are actively engaged in strategic endeavors such as launching new products, engaging in acquisitions, and forming partnerships to strengthen their foothold in the highly competitive market landscape.
In terms of market segmentation, the amines market can be categorized into various types including primary amines, secondary amines, tertiary amines, and specialty amines. Among these, primary amines are anticipated to maintain dominance in the market due to their extensive utilization across industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and personal care. Additionally, based on applications, the market can be segmented into agricultural chemicals, water treatment, personal care, cleaning products, and others, with the agricultural chemicals segment expected to witness substantial growth owing to the escalating demand for agrochemicals to enhance crop yield. Moreover, when segmented by end-use industry, the agriculture sector is projected to emerge as the largest consumer of amines, primarily driven by the necessity for fertilizers and pesticides.
Prominent market players such as BASF SE, The Dow Chemical Company, Akzo Nobel N.V., and Huntsman Corporation hold significant positions in the amines market. These key players are renowned for their diverse product portfolios, emphasis on innovation, sustainability initiatives, and continuous investments in research and development to enhance their offerings and cater to the evolving market demands. Their strategic focus on expanding market presence, improving product quality, and engaging in collaborations underscores their commitment to maintaining a competitive edge in the global amines market.
In conclusion, the future outlook for the global amines market appears promising, with sustained growth anticipated in the coming years. The market is expected to witness continued expansion driven by the ever-increasing demand for amines across a wide array of industries, supported by factors such as population growth, urbanization trends, and industrial development. Market players' strategic actions and investments are likely to further propel market growth and innovation, ensuring a dynamic and competitive landscape for the amines industry on a global scale.The global amines market is projected to witness robust growth in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for amines in various industries such as agriculture, pharmaceuticals, and chemicals. With factors like population growth, urbanization, and industrialization shaping the market landscape, the need for amines for applications like agrochemicals, water treatment, and personal care products is on the rise. Key market players such as BASF SE, The Dow Chemical Company, Akzo Nobel N.V., and Huntsman Corporation are at the forefront of the market, offering diverse product portfolios and focusing on innovation to meet evolving market demands. These companies are actively pursuing strategic initiatives such as product launches, acquisitions, and partnerships to enhance their market position and stay competitive in the global amines market.
In terms of market segmentation, the amines market can be categorized into different types, including primary amines, secondary amines, tertiary amines, and specialty amines. Primary amines are expected to remain dominant in the market due to their broad applications across various industries. When segmented by application, the market can be divided into agricultural chemicals, water treatment, personal care, cleaning products, and others. The agricultural chemicals segment is poised for significant growth due to the escalating demand for agrochemicals aimed at improving crop yield. Furthermore, the end-use industry segmentation of the amines market includes agriculture, pharmaceuticals, chemical, and others, with the agriculture sector emerging as the largest consumer of amines driven by the need for fertilizers and pesticides.
Looking ahead, the future outlook for the global amines market appears promising, with sustained growth expected as key market players continue to drive innovation and expansion in response to market dynamics. The market's growth trajectory is likely to be influenced by factors such as population expansion, urbanization trends, and ongoing industrial advancements, all of which contribute to the rising demand for amines across multiple sectors. Market players' strategic efforts and investments in research and development are anticipated to fuel further growth and foster a competitive landscape in the global amines market. The market's evolution is set to bring about new opportunities for innovation, collaboration, and market differentiation as companies strive to meet the evolving needs and demands of industries relying on amines for their operations.
Evaluate the company’s influence on the market
https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-amines-market/companies
Forecast, Segmentation & Competitive Analysis Questions for Amines Market
- What’s the estimated market worth of Amines Market globally?
- How is Amines Market growth distributed across regions?
- Which segment generates the highest revenue for Amines Market?
- What companies are discussed in the strategic landscape for Amines Market?
- Which countries are experiencing rapid adoption in Amines Market?
- Who are the globally recognized competitors in Amines Market?
Browse More Reports:
Global Organic Ice-Cream Market
Global Pet Food Flavors and Ingredients Market
Global Placental Stem Cells (PSCS) Market
Global Point of Care (POC) Urinalysis Market
Global Polymer Chameleon Market
Global Polystyrene Packaging Market
Global Quillaia Extracts Market
Global Renal Panel Testing Market
Global Retinal Biologics Market
Global Scratch-Resistant Glass Market
Global Surgical Instrument Tracking Systems Market
Global Transit Packaging Market
Global Veterinary Care Market
Global Wilson’s Disease Drugs Market
Global Yeast Protein Expression Service Market
About Data Bridge Market Research:
An absolute way to forecast what the future holds is to comprehend the trend today!
Data Bridge Market Research set forth itself as an unconventional and neoteric market research and consulting firm with an unparalleled level of resilience and integrated approaches. We are determined to unearth the best market opportunities and foster efficient information for your business to thrive in the market. Data Bridge endeavors to provide appropriate solutions to the complex business challenges and initiates an effortless decision-making process. Data Bridge is an aftermath of sheer wisdom and experience which was formulated and framed in the year 2015 in Pune.
Contact Us:
Data Bridge Market Research
US: +1 614 591 3140
UK: +44 845 154 9652
APAC : +653 1251 975
Email:- [email protected]
"
